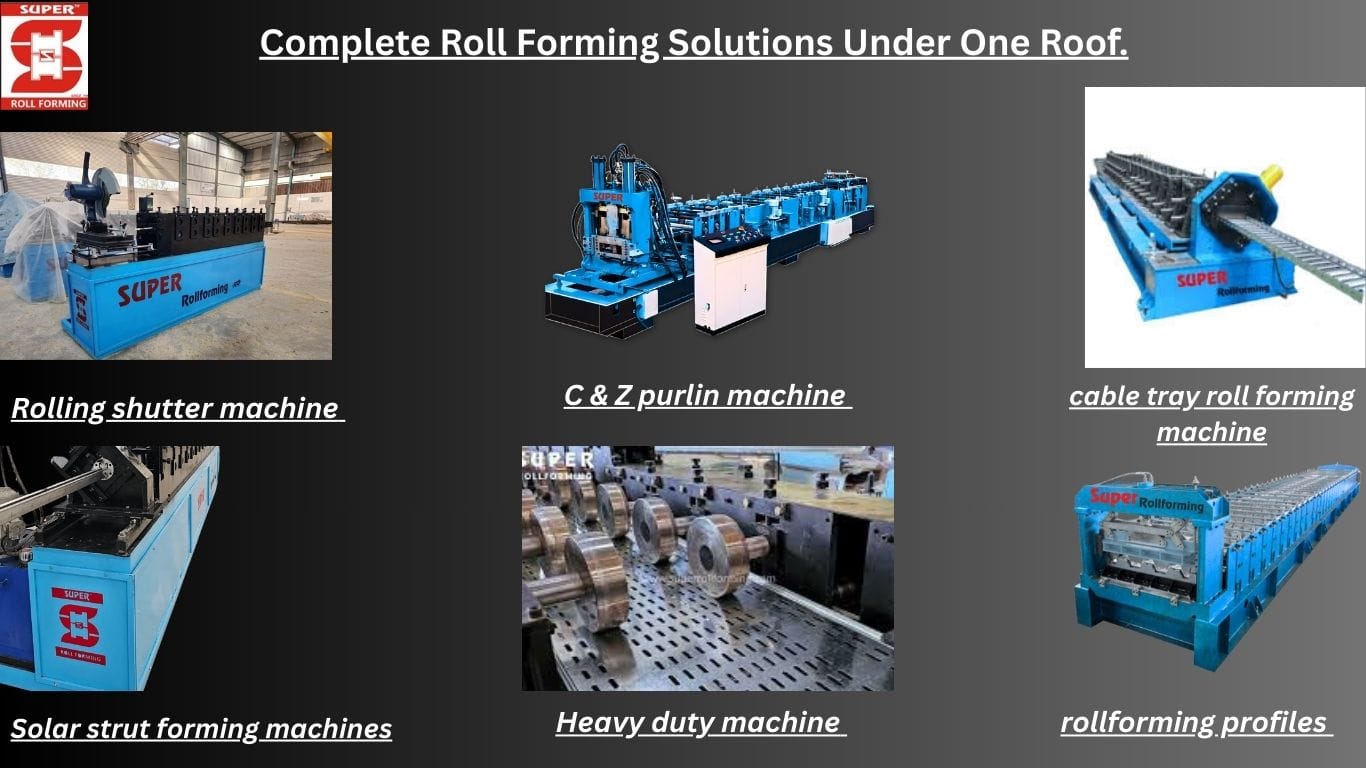
In the competitive world of manufacturing, the importance of prototyping cannot be overstated—especially in the realm of roll forming. As industries like automotive, construction, and renewable energy increasingly demand custom, precise, and durable metal parts, roll forming manufacturers must leverage effective prototyping to deliver cutting-edge products. This process enables companies to ensure design accuracy, test feasibility, and maximize product efficiency before mass production.
Why Prototyping Matters in Roll Forming
Prototyping plays a vital role in helping manufacturers create highly customized roll-formed products with minimal risk and cost. Here’s why it’s indispensable:
- Cost Savings: Prototyping enables design adjustments early, reducing errors in final production.
- Risk Reduction: Testing prototypes helps manufacturers avoid costly material waste and machinery downtime.
- Efficiency: Early-stage prototyping allows quick adjustments, accelerating time-to-market for new products.
Benefits of Prototyping in Roll Forming
1. Enhanced Design Precision
Roll forming is often used to create complex, customized profiles with precise tolerances. Prototyping allows for thorough testing of these designs:
- Precision Testing: Ensures that every bend, cut, and form adheres to the required specifications.
- Design Validation: Identifies potential issues in geometry, shape, or dimensions that may affect functionality.
2. Reduction in Production Costs
Developing roll-formed products can be costly, especially if errors arise during mass production. Prototyping helps mitigate these risks:
- Material Savings: Allows for adjustments before committing to expensive materials.
- Process Optimization: Tests different materials, gauges, and finishes, helping to identify the most cost-effective options.
- Tooling Costs: Detects design inconsistencies early, reducing the need for costly retooling.
3. Shorter Product Development Cycles
Prototyping allows manufacturers to quickly adjust and improve designs, helping them bring products to market faster:
- Iterative Process: Prototypes can be easily modified, allowing rapid iterations and testing.
- Time Efficiency: Reduces overall development time by resolving issues early.
The Prototyping Process in Roll Forming
Understanding the steps involved in the prototyping process for roll-formed products can clarify how it improves design and production:
Step 1: Initial Design and Material Selection
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Initial designs are created using CAD software, allowing precise modeling and simulations.
- Material Choice: Suitable materials are chosen based on the end-use, such as cold-rolled steel for its durability or aluminum for its lightweight properties.
Step 2: Prototype Fabrication
- Creating a Physical Sample: Using small-scale versions of roll-forming equipment, a sample product is made.
- Testing and Modifications: The prototype undergoes rigorous testing, and any issues are adjusted within the design.
Step 3: Prototype Evaluation and Validation
- Quality Checks: Ensures the prototype meets the specific requirements for shape, durability, and functionality.
- Customer Feedback: If applicable, customer input is gathered to align the product with market needs.
Step 4: Final Design Approval
Once the prototype meets all specifications, the final design is approved, and the production process begins. This ensures a seamless transition from prototype to full-scale manufacturing.
Key Prototyping Techniques in Roll Forming
Different prototyping techniques serve unique purposes, depending on the requirements of the roll-formed product:
- 3D Printing: Ideal for rapid prototyping, allowing manufacturers to test designs without investing in materials or equipment.
- Laser Cutting and Bending: Provides a high degree of accuracy for testing intricate designs and shapes.
- Metal Stamping: Used when testing specific sections or details of the design, especially for smaller components.
Challenges in Roll Forming Prototyping
While beneficial, prototyping in roll forming also presents certain challenges:
- Initial Costs: The upfront cost for materials and equipment can be high.
- Time-Intensive: Some complex designs may require multiple iterations before achieving the ideal prototype.
- Specialized Expertise: Roll forming requires skilled professionals who understand the intricacies of metal forming.
Trends in Prototyping for Roll Formed Products
The rise of advanced technologies has significantly impacted prototyping processes in roll forming:
Digital Twin Technology
Digital twin technology, where a digital replica of the product is created, enables real-time testing and analysis. This approach allows roll-forming companies to test designs virtually, reducing the need for physical prototypes.
Simulation Software
Advanced simulation software enables manufacturers to analyze a prototype’s performance under various conditions. This technology helps predict potential issues, further enhancing precision and reducing material costs.
Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is now widely used in prototyping to speed up the process. This method provides an affordable way to produce sample parts quickly, making it possible to test and refine designs before creating final metal prototypes.
Conclusion
Prototyping is a cornerstone of developing new roll-formed products, offering benefits from enhanced precision to cost efficiency. With the rise of digital tools and additive manufacturing, prototyping has become faster, more accurate, and more accessible. As a result, roll-forming companies can stay competitive, quickly adapt to industry demands, and consistently deliver high-quality products.
Incorporating prototyping into the development process is essential for creating innovative, functional, and durable roll-formed products that meet the highest standards. Embracing the latest prototyping techniques not only reduces risks and costs but also ensures a robust, streamlined approach to product development in the roll-forming industry.